Statistical analysis colouring-based
First of all I want to build an histogram of the metric values to understand better their distribution. I implemented the following code to do that:
bag := Bag new.
RTObject withAllSubclasses do:[:e| bag add: e numberOfMethods].
res := ((0 to: bag max) collect:[:v| v @ (bag select:[:va| va = v]) size ]).
b := RTGrapher new.
b extent: 300 @ 300.
ds := RTDataSet new.
ds dotShape ellipse color: (Color blue alpha: 0.5).
ds points: (0 to: bag max).
ds connect.
ds y: [ :v | (res select:[:va| va x = v ]) first y ].
b add: ds.
b axisXWithNumberOfTicks: 10.
b axisYWithNumberOfTicks: 10.
b build.The result is shown in the picture below:
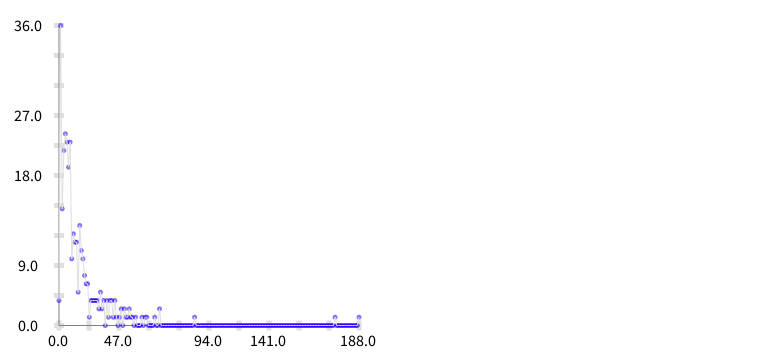
The next step is to build a function that approximates to these data. In consequence I built a polynomial regression (using the least square method) thanks to the SciSmalltalk project. To load SciSmalltalk do:
Gofer new
url: 'http://www.smalltalkhub.com/mc/SergeStinckwich/SciSmalltalk/main';
package: 'ConfigurationOfSciSmalltalk';
load.
(Smalltalk at: #ConfigurationOfSciSmalltalk) loadDevelopment.Therefore, the code below uses it to build the approximation.
|estimation|
fit := DhbPolynomialLeastSquareFit new:8.
bag := Bag new.
RTObject withAllSubclasses do:[:e| bag add: e numberOfMethods].
(0 to: bag max)
do:[:v| fit add: (DhbWeightedPoint
point: v @ (bag select:[:va| va = v]) size) ].
estimation := fit evaluate.
b := RTGrapher new.
b extent: 300 @ 300.
ds := RTDataSet new.
ds dotShape ellipse color: (Color blue alpha: 0.5).
ds points: (0 to: bag max).
ds connect.
ds y: [ :v | estimation value: v ].
b add: ds.
b axisXWithNumberOfTicks: 10.
b axisYWithNumberOfTicks: 10.
b build.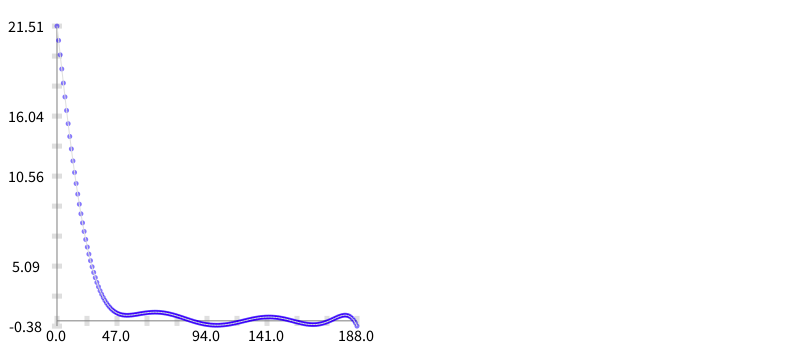
Now we can use the polynomial function with a standard metric normaliser. The code below applied this idea to the original visualisation:
|estimation|
fit := DhbPolynomialLeastSquareFit new:8.
bag := Bag new.
RTObject withAllSubclasses do:[:e| bag add: e numberOfMethods].
(0 to: bag max)
do:[:v| fit add: (DhbWeightedPoint
point: v @ (bag select:[:va| va = v]) =size) ].
estimation := fit evaluate.
v := RTView new.
objs := RTObject withAllSubclasses.
els := RTBox new height:#numberOfMethods; color:[Color red]; elementsOn: objs.
v addAll: els.
RTEdgeBuilder new
view: v;
objects: objs from: [ :entry | entry superclass ].
RTMetricNormalizer new
elements: els;
normalizeColor: #numberOfMethods
using: {Color black . Color green . Color black}
using:[:v| estimation value: v ].
RTTreeLayout on: els.
els @ RTPopup.
v @ RTDraggableView.
v open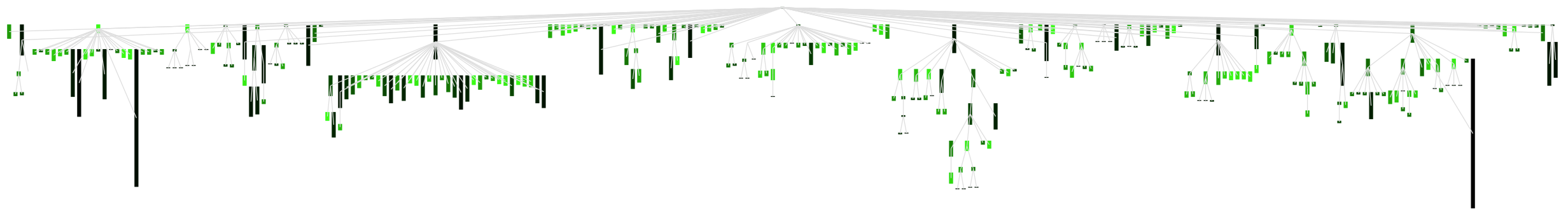 Right-click on the image and open it in a new window for a larger picture
Right-click on the image and open it in a new window for a larger picture
The following animated GIF (@http://gifmaker.cc) shows the differences between the original approach and the statistical based one.
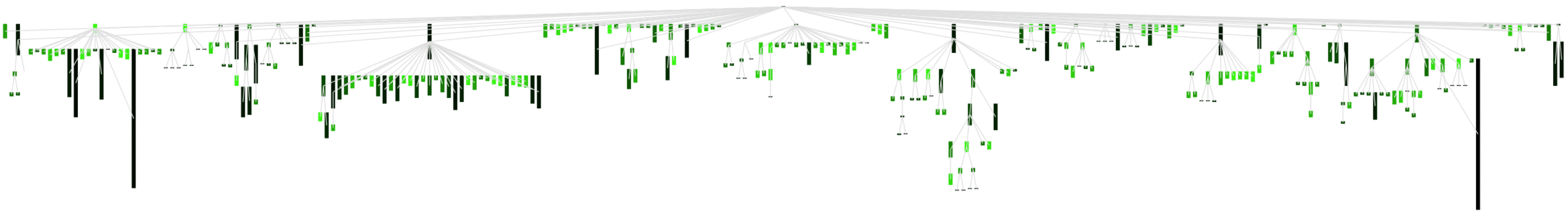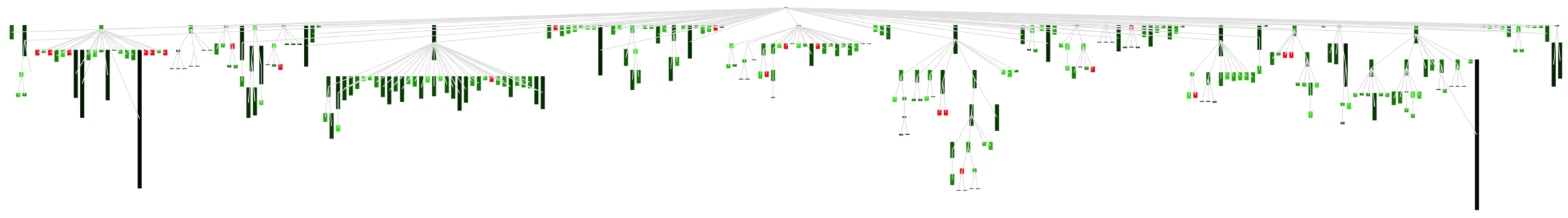 Right-click on the image and open it in a new window for a larger picture
Right-click on the image and open it in a new window for a larger picture
Statistical-based approach characteristics:
- It does take into account distribution of metric values.
- Useful for detecting distant values from 'the center'
- Not too useful for finding maximum values
This approach seems more useful if highlighting the median.
The following code implements a visualisation clustering the values in four quartiles (assigning different intensities of green) and highlights the nodes that match one of the values splitting the quartiles (including the median).
v := RTView new.
objs := RTObject withAllSubclasses.
nums := objs collect: #numberOfMethods.
median := nums median.
median2 := (nums reject:[:e| e < median]) median.
median1 := (nums reject:[:e| e > median]) median.
els := RTBox new
height: [ :e | e numberOfMethods ];
color: [ :e |
e numberOfMethods < median1
ifTrue: [Color green]
ifFalse: [
e numberOfMethods <= median
ifTrue: [ Color r: 0 g: 0.75 b: 0 ]
ifFalse: [
e numberOfMethods <= median2
ifTrue:[Color r: 0 g: 0.5 b: 0 ]
ifFalse:[Color r: 0 g: 0.25 b: 0] ] ]];
borderColor:[:e|
((Array with: median with: median1 with: median2)
includes: e numberOfMethods)
ifTrue:[Color red]
ifFalse:[Color white]
];
elementsOn: objs.
v addAll: els.
RTEdgeBuilder new
view: v;
objects: objs from: [ :entry | entry superclass ].
RTTreeLayout on: els.
els @ RTPopup.
v @ RTDraggableView.
v openThe result is shown in the picture below.
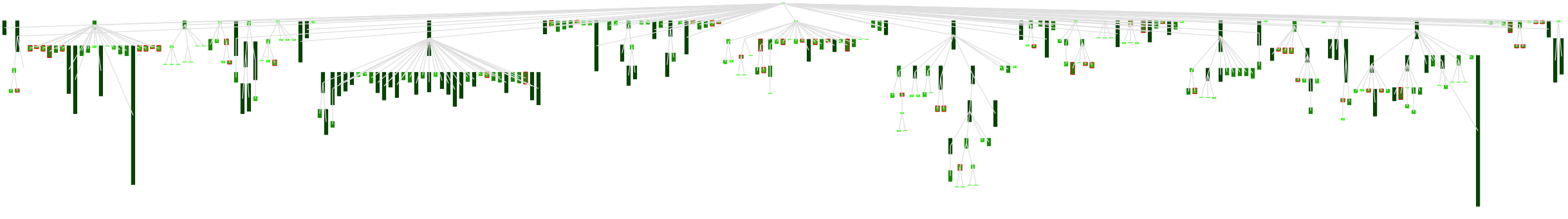 Right-click on the image and open it in a new window for a larger picture
Right-click on the image and open it in a new window for a larger picture